Making Existing ERC20 Assets Cross-chain Compatible
If you would like to make an existing ERC20 asset cross-chain compatible, it's quite simple, following the instructions below
XC20+ Extension
In short, the XC20 standard allows smart contracts to interact with cross-chain compatible assets, as if they were typical ERC20 assets.
Unlike standard ERC20 assets deployed within the EVM environment, where balances, issuance, etc. are stored directly, XC20 assets are mapped to a Substrate pallet, which means that developers do not have access to the same logic inherent to ERC20 format, such as _mint or _burn.
In general, this is fine for existing XC20 assets since we shouldn't be minting or burning them in smart contracts (e.g. there is no valid reason to mint cross-chain DOT on Astar). However, there are use cases where having an extended set of functionalities is useful and required, such as for wrapped tokens.
For this reason, we provide an extended XC20 interface called XC20+. It provides the following methods:
// Used to check what is the existential deposit of XC20 asset
function minimumBalance() external view returns (uint256);
// Used to mint new funds
function mint(address beneficiary, uint256 amount) external returns (bool);
// Used to burn funds
function burn(address who, uint256 amount) external returns (bool);
The aforementioned list could be extended in the future.
Please note that minting and burning requires certain priviliges - read about XC20 assets to learn more.
Please note that the burn() function in XC20+ is inhereting the behaviour of pallet-assets burn() function. Calling pallet-assets burn() function with a amount higher than the current balance will result in a burn of the amount available, and returning success.
In contracts, the burn() implementation in ERC20Burnable.sol will burn the amount if it is lower or equal to the account's balance.
Wrapped Tokens
A wrapped token is a token whose value is tied to an underlying cryptocurrency. An amount of the original token is locked in a digital vault, and in return allows an equivalent amount of wrapped tokens to be minted.
This is useful for several reasons, to mention a few:
- To extend the functionalities of an existing token in conjunction with other ERC20 modules.
- To allow a native cryptocurrency to behave like an ERC20, e.g. Wrapped Ether (WETH).
- To allow the use of currencies outside their native blockchain, e.g. Wrapped bitcoin (WBTC).
In the next example we will examie how to wrap an existing ERC20 token into XC20.
Wrapping ERC20 into XC20
In this example, the underlying token will be an existing ERC20, called BURRITO. We want to wrap some BURRITOs and make them cross-chain-ready. Using a standard ERC20Wrapper token spec from OpenZeppelin will not be enough. Therefore we will need to override some of the ERC20Wrapper functions, and use XC20+ functions. Let's call the newly wrapped token xcBURRITO. xcBURRITO takes the address of the underlaying token (BURRITO) and the newly created asset's address as constructor parameters. And we’ll set values for the other required parameters, but notice that we have to include the ERC20Permit constructor call, because xcBURRITO is now a parent of BURITTO.
constructor(IERC20 burrito)
ERC20("Wrapped Burrito", "xcBUR")
ERC20Permit("Wrapped Burrito")
ERC20Wrapper(burrito)
{}
Since we can't use ERC20Wrapper out of box we'll override it and use the XC20+ interface.
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/extensions/ERC20Wrapper.sol";
import "./Burrito.sol";
contract XcBurrito is Xc20Plus, ERC20Wrapper, BURRITO{
constructor(IERC20 burrito)
Xc20Plus("Wrapped Burrito", "xcBUR")
ERC20Permit("Wrapped Burrito")
ERC20Wrapper(burrito)
{}
function _mint(address _to, uint256 _amount)
internal
override(ERC20)
{
// add here your pre-mint hooks if needed
require(
IERC20Plus(xcBurrito).mint(_to, _amount), "Minting xc token failed"
);
// add here your post-mint hooks if needed
}
}
Procedure
1. Create an XC20 asset
Follow the documentation on how to Create XC20 Assets.
2. Deploy the xcBurrito.sol smart contract
To deploy the XcBurrito contract you will need 2 input parameters
- Burrito ERC20 token address (H160)
- XC20 asset address (H160)
- Follow the instructions about how to Calculate an XC20 Address. For example, if the asset_id is 17 (=0x11), the resulting EVM address will be
0xffffffff00000000000000000000000000000011
- Follow the instructions about how to Calculate an XC20 Address. For example, if the asset_id is 17 (=0x11), the resulting EVM address will be
3. Transfer XC Asset Ownership to the xcBurrito Smart Contract
To allow the xcBurrito contract to be able to mint/burn you need to call the setTeam() extrinsic on pallet-assets, and configure the issuer and admin to be xcBurrito. This will allow the contract to issue wrapped XC20 assets, but since the EVM contract has 24 bytes (H160), we will need to transform the EVM address to ss58 format before we can call the extrinsic.
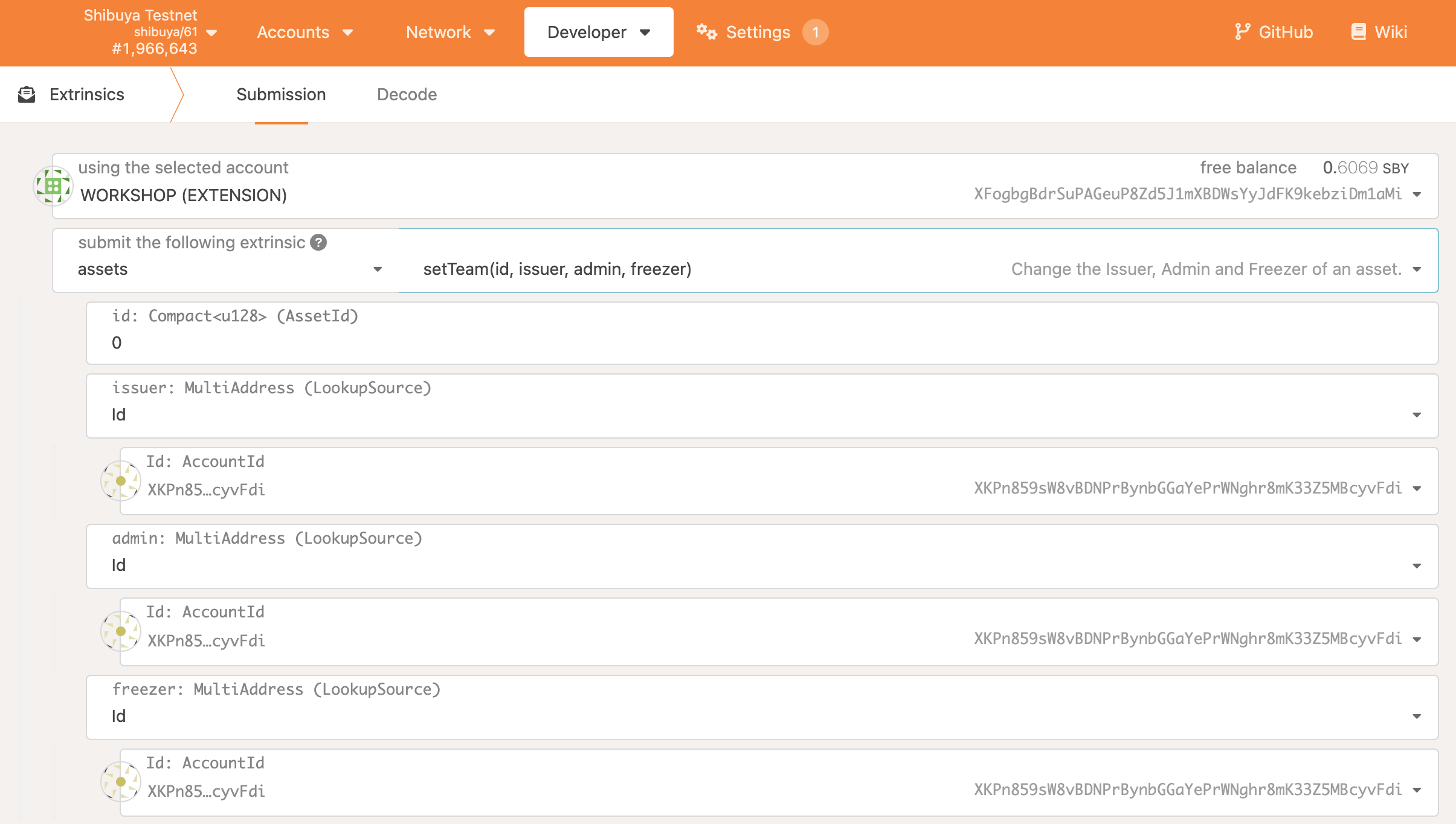
You can renounce ownership of the XC20 by calling the transferOwnership() extrinsic on pallet-assets. Do note that after calling the extrinsic, you will no longer be able to
change the issuer or admin parameters, so you will want to ensure they are set correctly.
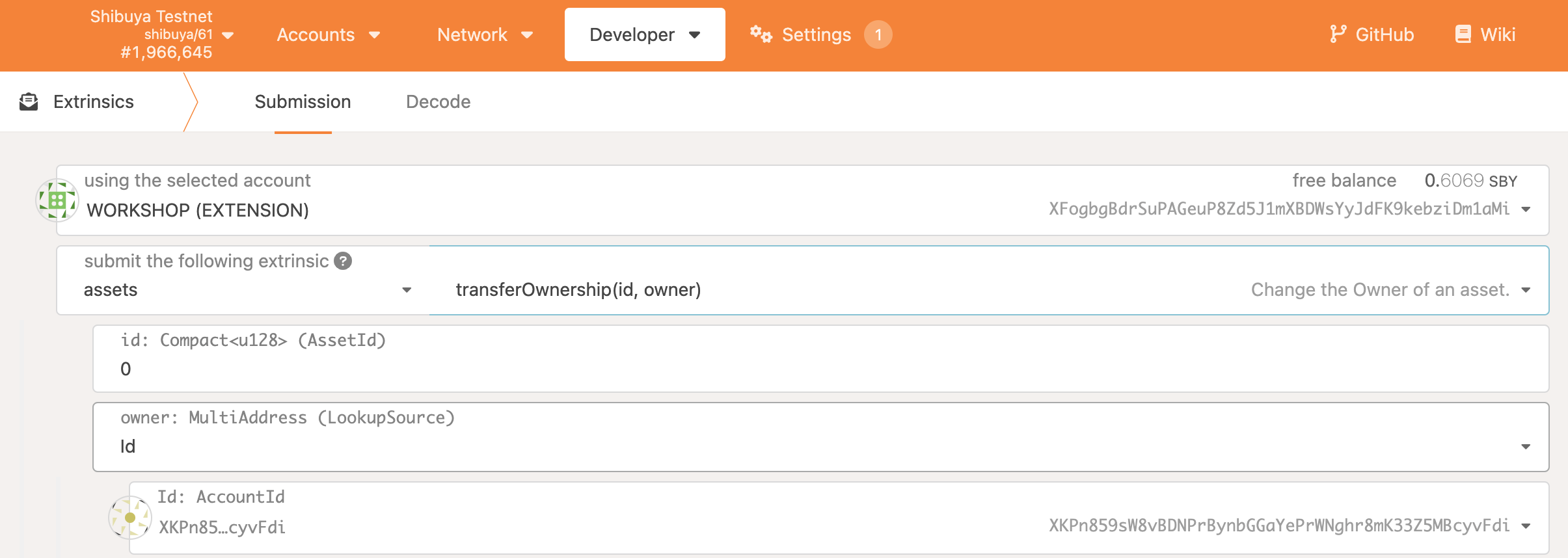
Now the xcBurrito contract is able to mint XC20 tokens for callers who own Burrito ERC20 tokens.
User Actions
To convert Burrito tokens into xcBurrito assets, users will need to perform the following actions.
- Approve the xcBurrito smart contract to transfer ERC20 Burrito tokens from a user's balance, to the xcBurrito contract. As an alternative, the
permit()call can be used to improve UX. - User calls xcBurrito
depositFor()for minting new XC20 tokens, orwithdrawTo()for burning XC20 tokens. - The newly wrapped assets are able to be transferred between chains, like any other XC20 asset (please see the XCM documentation for more details).
End result
The result of depositFor(user, amount) will be:
- XcBurrito locks an
amountof ERC20 Burrito token. - User's balance of ERC20 Burrito is decreased by
amount - XcBurrito contract mints the same
amountof xcBurrito assets - User's balance of xcBurrito asset is increased by
amount
The result of withdrawTo(user, amount) will be:
- XcBurrito contract burns an
amountof XcBurrito asset - User's balance of xcBurrito asset is decreased by
amount - XcBurrito contract transfers
amountof ERC20 Burrito token to user - User's balance of ERC20 Burrito is increased by
amount